|
Effects of Acid Rain
One of the most serious impacts of acid precipitation
is on forests and soils. Great damage is done when sulfuric acid
falls onto the earth as rain. Nutrients present in the soils are
washed away. Aluminum also present in the soil is freed and the
roots of trees can absorb this toxic element. Thus, the trees are
starved to death as they are deprived of their vital nutrients such
as calcium and magnesium. Not all of the sulfur dioxide is converted
to sulfuric acid. In fact, a substantial amount can float into the
atmosphere, move over to another area and return to the soils unconverted.
As this gas returns back to earth, it clogs up the stomata in the
leaves, thus hindering photosynthesis.
One of the direct effects of acid rain is
on lakes and its aquatic ecosystems. There are several routes through
which acidic chemicals can enter the lakes. Some chemical substances
exist as dry particles in the air while others enter the lakes as
wet particles such as rain, snow, sleet, hail, dew or fog. In addition,
lakes can almost be thought of as the "sinks" of the earth, where
rain that falls on land is drained through the sewage systems eventually
make their way into the lakes. Acid rain that falls onto the earth
washes off the nutrients out of the soil and carries toxic metals
that have been released from the soil into the lakes.
Animals'
pH Tolerance Graph
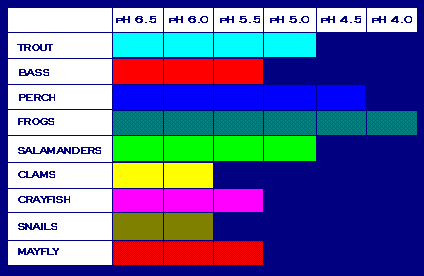
Acid rain also damages materials such as
fabrics. For example, flags put up outside are being "eaten away"
by the acidic chemicals in the precipitation. Books and age-old
art that are centuries old are also being affected. The ventilation
systems of the libraries and museums that hold them do not prevent
the acidic particles from entering the buildings and so, they get
in and circulate within the building, affecting and deteriorating
the materials.
Among the serious side effects of acid pollution
on humans, one of the worst is the respiratory problems. The SO2
and NO2 emissions give rise to respiratory problems such as asthma,
dry coughs, headaches, eye, nose and throat irritations. An indirect
effect of acid precipitation on humans is that the toxic metals
dissolved in the water are absorbed in fruits, vegetables and in
the tissues of animals. Although these toxic metals do not directly
affect the animals, they have serious effects on humans when they
are being consumed. For example, mercury that accumulates in the
organs and tissues of the animals has been linked with brain damage
in children as well as nerve disorders, brain damage and death.
Similarly, another metal, Aluminum, present in the organs of the
animals, has been associated with kidney problems and recently,
was suspected to be related to Alzheimer's disease.
Some of the constituents of acid pollution
are sulfates, nitrates, hydrocarbons and ozone. These exists as
dry particles in the air and contribute to haze, affecting visibility.
This makes navigation especially hard for air pilots. Acid haze
also interferes with the flow of sunlight from the sun to the earth
and back. In the Arctic, this affects the growth of lichens, which
in turn affect the caribou and reindeer that feed on it.
|

